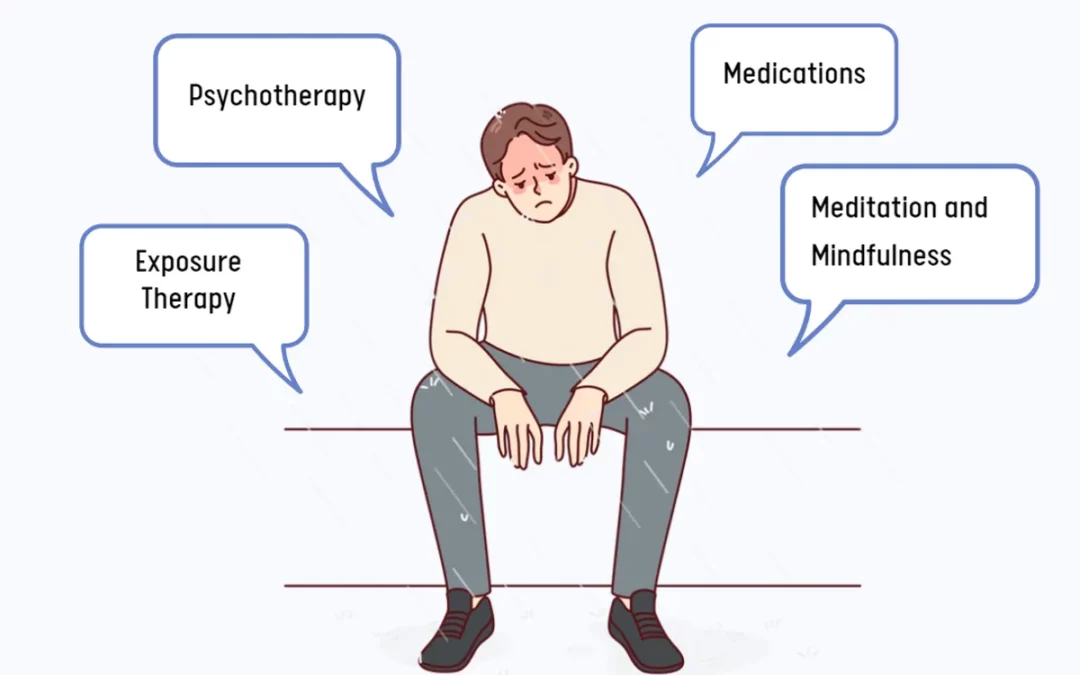
Roughly between 7–8% of the population will suffer from PTSD at some point in their lives. For individuals struggling to cope with symptoms, understanding effective coping strategies is crucial. This post is part of a series on techniques, strategies, and self-care to manage PTSD and maintain emotional health.
Understanding PTSD
PTSD is diagnosed by various symptoms like memory intrusion, flashbacks, recurring dreams, and increased anxiety following traumatic events. It can drastically affect a person’s life, impacting work, relationships, and overall quality of life. According to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, about 11 to 20 percent of veterans from the Iraq and Afghanistan wars have been diagnosed with PTSD due to combat experiences.
Recognizing PTSD Symptoms
Successfully managing PTSD starts with understanding common symptoms. These symptoms generally fall into four categories:
- Reexperiencing or Retraumatisation: Recurring memories or distressing flashbacks of the traumatic event.
- Avoidance: Avoiding people, places, or activities that trigger memories of the trauma.
- Negative Mood and Thought Changes: Feelings of hopelessness or persistent self-criticism.
- Increased Arousal: Heightened vigilance, irritability, sleep problems, and exaggerated startle responses.
Identifying these symptoms can guide individuals toward support and coping strategies.
Revealed Strategies for Coping with PTSD
Therapy for PTSD
Counseling is a valuable tool for managing PTSD, with several effective therapeutic approaches, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A structured approach linking thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, shown to reduce PTSD symptoms in 60-80% of cases.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): A method for directly processing traumatic memories under a therapist’s guidance.
- Trauma-Informed Therapy: Creating a safe, supportive environment for patients to discuss their experiences without re-traumatization.
Mindfulness Practices
Weekly mindfulness training helps manage PTSD by allowing individuals to observe their thoughts without judgment, promoting presence in the moment. Techniques like deep breathing, grounding exercises, and body scanning have proven effective in reducing anxiety and promoting well-being.
The Role of Physical Activity and Nutrition
Physical activity releases endorphins that positively impact mood, with studies showing regular exercise can reduce anxiety and depression symptoms by 25%. Nutrition is also vital—foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals support brain health, while a well-balanced diet can help combat stress.
Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene, including a regular sleep schedule and a relaxing bedtime routine, is essential for those with PTSD. Improved sleep quality has been linked to lower PTSD symptoms, making restful sleep a cornerstone of recovery.
Building a Strong Support System
Support Groups
Support groups offer individuals the chance to share their experiences with others who understand, fostering emotional regulation and a sense of community.
Family and Friends
Educating family and friends about PTSD helps create a supportive environment, alleviating feelings of isolation for those affected.
Resilience Building
Resilience is crucial in dealing with PTSD. Key resilience-building techniques include:
- Positive Self-Talk: Encouraging oneself with affirming statements to combat negative thoughts.
- Goal Setting: Establishing goals provides focus and hope during recovery.
- Cultivating Gratitude: Practicing gratitude through journaling can shift focus from negative aspects to the positive ones in life.
Raising Mental Health Awareness
Awareness of PTSD and its impact is vital in breaking stigmas and motivating individuals to seek treatment. Education efforts at schools, workplaces, and in the community can spread knowledge on PTSD symptoms and available treatments.
Workplace Support
Employers can implement mental health policies and resources, showing a commitment to employees’ well-being, which has been linked to higher job satisfaction.
Community Involvement
Community-based mental health advocacy programs provide support and resources for PTSD sufferers, educating them on coping techniques.
Policy Change and Mental Health Funding
Advocating for increased funding for mental health and PTSD treatment can lead to broader support for those in need, encouraging a holistic approach to recovery.
A Holistic Approach to PTSD Treatment
Given the complex nature of PTSD, holistic approaches to coping are becoming essential. Therapy, mindfulness, self-care, and strong support systems offer the necessary tools for managing PTSD beyond medication alone.