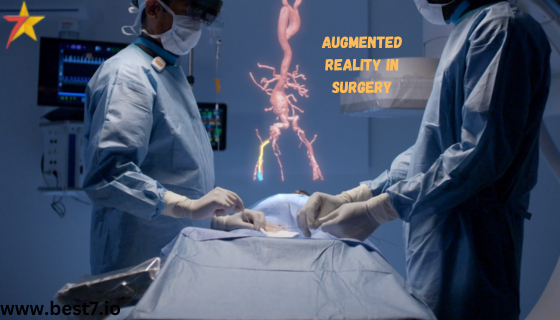
Surgical procedures are expected to be among the first to be revolutionized by AR, offering additional perspectives for complex operations in the near future. With constantly improving medical technology, AR will become more relevant in operating rooms, providing enhanced precision, training methods, and patient outcomes. The potential influence of augmented reality in surgery is predicted to reshape challenging operations and redefine how surgeons engage with their patients.
Augmented Reality in Surgery: An Overview
Augmented Reality (AR) depicts the real world with additional computer-generated images, overlaying extra information on top of reality. In surgery, AR is used to show surgeons real-time, augmented images of patients. When 3D imaging and live data are integrated with surgical videos, they become powerful tools that guide surgeons for better decision-making and outcomes.
The Growing Market for AR in Healthcare
The global market for augmented reality in healthcare is projected to reach approximately USD 2.4 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by the demand for advanced solutions in medical treatments. As AR technologies continue to evolve rapidly, their integration into surgical procedures is expected to offer numerous advantages across diverse clinical scenarios.
Precision in Surgery with Augmented Reality
AR enhances surgical precision by bringing 3D digital models of a patient’s anatomy directly onto the surgical field. This eliminates reliance on traditional devices and reduces potential errors. Particularly effective for minimally invasive surgeries, AR supports efficient, low-risk procedures, helping surgeons avoid vulnerable anatomical structures while improving overall patient outcomes.
Real-Time Data Integration for Improved Decision-Making
Real-time data integration during surgeries is a key advantage of AR. Vital signs and imaging data can be displayed live over the surgical field, enabling better situational awareness. For instance, in complex cardiac surgeries, AR displays real-time metrics like heart rate and blood pressure, allowing surgeons to adapt rapidly to changes and enhance patient safety.
Transforming Surgical Training and Learning
AR is set to revolutionize surgical training by providing virtual simulations that allow students and residents to practice high-risk procedures in a risk-free environment. This technology offers interactive 3D visualizations of human anatomy, boosting confidence and competence in performing complex techniques. Comprehensive AR training modules are equipping learners to handle a variety of surgical scenarios effectively.
Integrating AR with Robotic Surgery Systems
The future of robotic surgery systems will be closely tied to augmented reality. By integrating AR, surgeons gain real-time visualization of the surgical field, enhancing precision and control during robotic-assisted procedures. This synergy has been shown to shorten surgical times and improve outcomes in complex cases.
Enhancing Surgical Planning and Navigation
Augmented reality supports preoperative surgical planning by converting CT and MRI scans into interactive 3D models. Surgeons can “visualize” their strategy before entering the operating room, streamlining complex procedures. AR also enhances intraoperative navigation by overlaying critical information, helping surgeons navigate through challenging anatomical landscapes with accuracy.
Patient Safety and Engagement with AR
AR fosters safe patient care by providing detailed insights to reduce surgical risks and improve outcomes. It also enhances patient engagement by offering visual aids to explain procedures, increasing comprehension and satisfaction. This builds trust between patients and healthcare providers, leading to better overall care experiences.
The Future of AR in Healthcare
As AR technologies evolve, their integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning will expand their potential in healthcare. Future advancements are expected to make AR systems more affordable and accessible, enabling even smaller healthcare facilities to adopt this transformative technology.
Addressing Challenges in AR Adoption
Despite its benefits, AR adoption in surgery faces challenges, including high costs, the need for extensive training, and concerns over patient data privacy. Addressing these issues through regulations, training programs, and cost-effective solutions will be crucial to realizing the full potential of AR in surgical practices.












