As technology changes in a blink of an eye, the future of data processing across the entire planet will be on the cusp soon, with edge computing taking over traditional cloud solutions to extensible decentralized computing infrastructures.
The demand for faster and more efficient data processing is fueling the rise of edge computing, particularly when it comes to real-time analytics and reduced latency applications. What this article hopes to do is to look at the opportunity edge computing presents and its potential impact across different sectors.
What is Edge Computing? Processing Data Near the Source
Edge computing means processing data at the edge of the network, near the source of data generation. By moving the architectural processing of data closer to the edge itself, organizations can now achieve faster data processing and reduce the proximity that a piece of data needs to travel.
Gartner states that 75% of enterprise-generated data will be created and processed outside a traditional centralized data center by 2025. Such an outlook underscores that edge computing is increasingly being viewed as a key facet of the evolving data processing landscape.
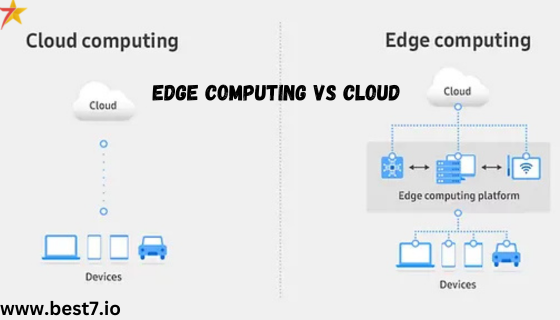
Cloud vs Edge Computing: Addressing Latency and Bandwidth Challenges
The direct comparison of cloud vs edge computing highlights why using edge technology is beneficial only for exact work. With cloud computing, while you get scalability as well as resource flexibility, there are also issues encountered on fronts of latency and bandwidth. Meaning data has to pass through the network, which can slow down performance, especially if you are working in real-time cases.
Edge computing solves these downsides by processing the data on the device itself, facilitating quick responses to user actions and a greatly improved user experience. For example — industries such as manufacturing and healthcare can benefit hugely from real-time processing potential to support immediate decision-making and thereby improve operational efficiency.
Supporting IoT: A Crucial Role for Edge Computing
One of the most popular edge computing benefits is that it also supports IoT. As the number of Internet of Things devices grows, millions more will need quick processing of a huge amount of data. This is because reportedly over 30 billion connected IoT devices are estimated by 2025.
Edge computing, such as the processing of IoT device data at or near an on-site location without having to transmit large volumes of data into the cloud, speeds up data processing, alleviating network congestion, and providing more reliability and efficiency in IoT ecosystems.
Edge Analytics: Real-Time Data Insights for Improved Decision-Making
Edge analytics allows for real-time data analysis at the edge, which generates faster insights. For instance, in smart cities, edge computing could be used to monitor traffic flow in real-time, resulting in dynamic traffic management and increased public safety.
Cisco says 94% of organizations that deployed edge and fog computing technologies achieved improved operational efficiency during the last six months of the pandemic. This number underscores the benefits of the transformational agility edge technology delivers, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to a dynamic environment.
Edge Computing Across Industries: From Transportation to Healthcare
Edge computing applications cut across different industries like transportation, healthcare, and retail. In transportation, edge computing is likely to be used for self-driving cars, which need edge devices and real-time data processing at the edge to operate correctly.
Connected vehicles, for example, will use edge computing to process sensor data as it is captured, allowing near-instantaneous decision-making in complicated driving situations. The global edge computing in the automotive market is expected to surpass USD 9 billion by 2030 as the need for real-time processing capacity for improving vehicle safety and efficiency increases.
Transforming Healthcare: Edge Computing and Telemedicine
Edge computing is a crucial part of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring in healthcare. With real-time patient data processing, providers can access AIOps capabilities at the edge, providing intelligence insights proactively — ensuring better patient outcomes. Processing biometric data at the edge, such as with wearable health devices, can give instantaneous alerts to healthcare professionals in case of abnormalities.
This not only improves the quality of patient care but also lightens the load on healthcare systems, reducing in-hospital visits and emergency interventions.
AI at the Edge: The Future of Smart Devices
Edge computing is predicted to become more involved in the world of AI (artificial intelligence). AI at the edge will enable sensors with machine learning algorithms to run on devices, allowing them to analyze data in real-time.
It will be especially useful in sectors like manufacturing, where predictive maintenance can be enabled by monitoring equipment performance. A DBS Bank research report identifies edge AI as a top trend to watch, while Markets and Markets projects the market to be worth billions by 2026, illustrating the overlapping trajectory of these technologies.
Edge Computing and Financial Services: A Game-Changer for Trading
Industries that depend on real-time data processing, such as the financial sector, will need edge computing to reduce latency. For instance, edge computing solutions will make it easier for high-frequency trading algorithms in the financial sector to perform faster and better on stock exchanges.
Processing trades and market data at the edge allows firms to respond to market changes faster, leading to higher profitability. A Deloitte survey found that 88 percent of financial services executives agree that edge computing will give their firms a competitive advantage.
Building a Resilient Edge Computing Infrastructure
To power the explosion of edge solutions, significant investment and development must go into edge computing infrastructure. This will require organizations to establish a resilient network of edge devices, gateways, and servers that work together for quick data processing. Increased need for cybersecurity up the stack is also a major concern.
As edge computing trends grow more mature, so must cybersecurity. The data processed at the edge needs to be encapsulated and protected with robust security measures to combat possible threats and vulnerabilities.
Personalized Retail Experiences: How Edge Computing is Shaping the Future
Edge computing solutions are built for narrow use cases to better align strategies with unique business requirements. In retail, edge computing can be used for inventory management, analyzing sales demand, and monitoring customer activity in real time.
This allows retailers to adapt stock levels according to market demand, leading to less waste and higher customer satisfaction. The increasing demand for personalized shopping experiences is expected to be a major factor driving the growth of edge computing in the retail market.
A Decentralized Future: Edge Computing, AI, and IoT
With the growing trend of decentralized computing, edge computing will not be limited to a single industry. Edge computing, AI, and IoT will help create smart ecosystems where different devices seamlessly communicate. This interconnectedness will allow for more efficient resource utilization, a higher degree of sustainability, and ultimately, an improvement in the quality of life.
Accelerating Research and Environmental Conservation with Edge Computing
In research, edge computing will facilitate high-level scientific experiments, such as climate simulations and real-time environmental observations. Data processing from sensors deployed across various locations will help researchers track key ecological changes and inform decision-makers in environmental conservation efforts. This will accelerate research and contribute to better management of natural resources.
The Future of Data Processing: Cloud to Edge Transition
To sum up, data processing is expected to enter a new era where the move from cloud to edge computing will revolutionize how data is processed. Edge computing offers much faster and more efficient data processing across all industries.
These savings in terms of latency, real-time analytics, and efficiency will grow further in significance as organizations look to new edge computing solutions. The future of edge computing is poised to revolutionize the way data is processed, opening exciting new opportunities for improvements in our daily lives and pushing technology forward.












